ECG Classification for Atrial Fibrillation, Normal Sinus Rhythm, and Congestive Heart Failure
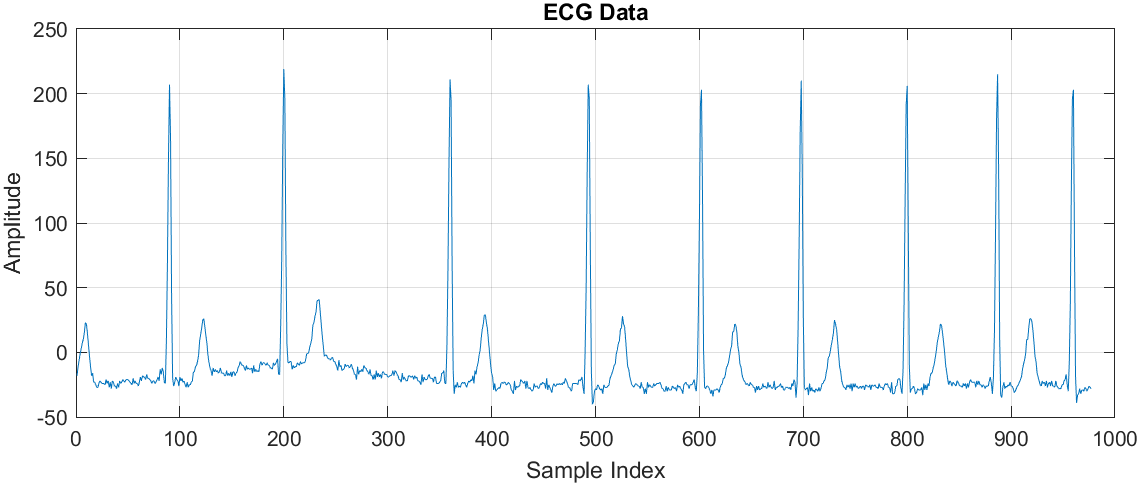
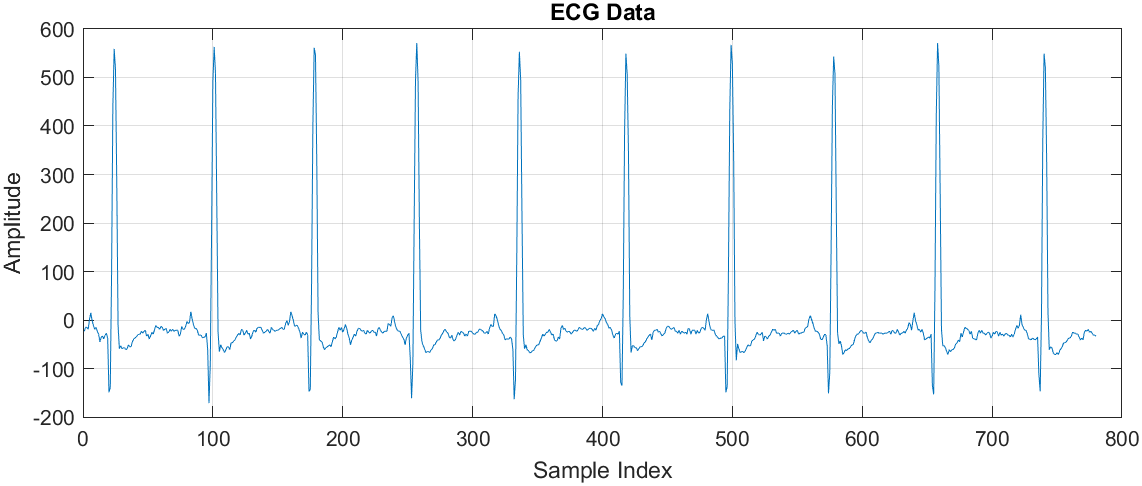
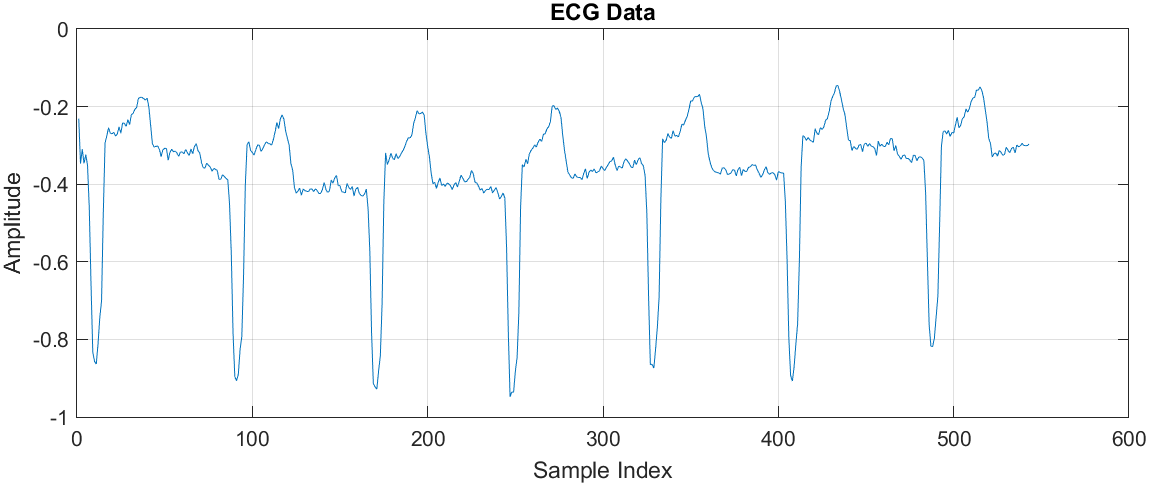
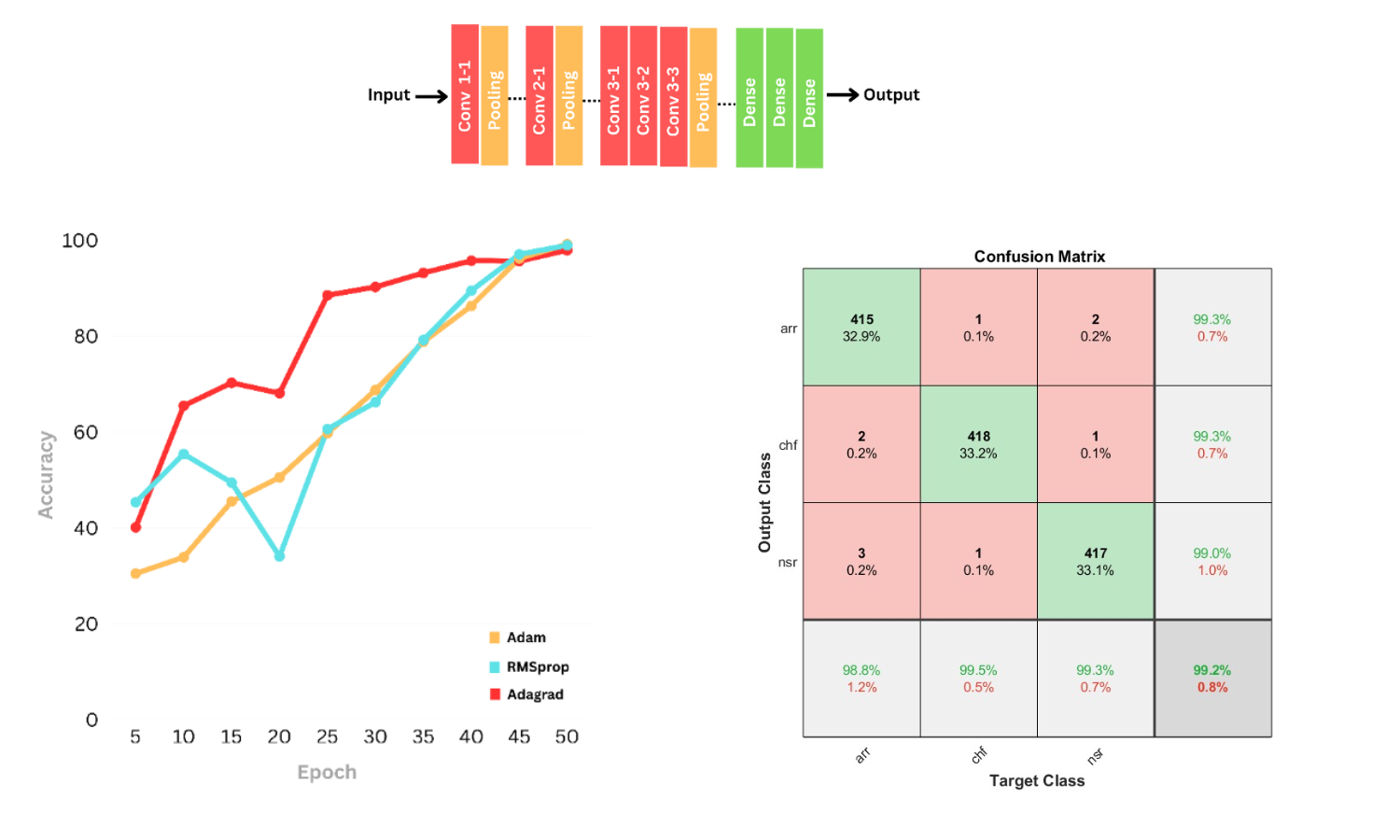
This research explores the use of deep learning for electrocardiogram (ECG) classification, focusing on distinguishing between Atrial Fibrillation (AF), Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR), and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF). The study proposes an AlexNet-based convolutional neural network (CNN) for accurate ECG signal classification. The model achieves an impressive 99.21% accuracy, outperforming traditional approaches. The paper details the preprocessing techniques, feature extraction, and ECG signal transformation into 2D images, which enhance model performance. The dataset is derived from the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database, ensuring clinical relevance.
Key Contributions
-Proposed a Deep Learning Model: Designed a CNN based on AlexNet architecture optimized for ECG signal classification.
-Data Preprocessing & Signal Transformation: Applied Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), Butterworth filtering, and wavelet transforms to convert 1D ECG signals into 2D images for deep learning analysis.
-Comparison of Architectures: Evaluated Custom CNN, VGG16, and AlexNet, with AlexNet achieving the highest accuracy (99.21%).
-Feature Engineering & Augmentation: Implemented stain augmentation, noise filtering, and signal denoising to improve classification robustness. High Performance Metrics: Achieved precision, recall, and F1-score above 99%, demonstrating the model’s clinical applicability.
The study confirms that deep learning can significantly improve ECG classification for early detection of cardiac conditions. Future work includes expanding the dataset, integrating multi-class classification for additional arrhythmias, and developing real-time ECG monitoring systems using edge AI.